Krf2 Intermolecular Forces
G 2 strands of DNA. Intermolecular Forces Permanent dipole-dipole forces Permanent dipole-dipole forces occurs between polar molecules It is stronger than London forces and so the compounds have higher boiling points Polar molecules have a permanent dipole.
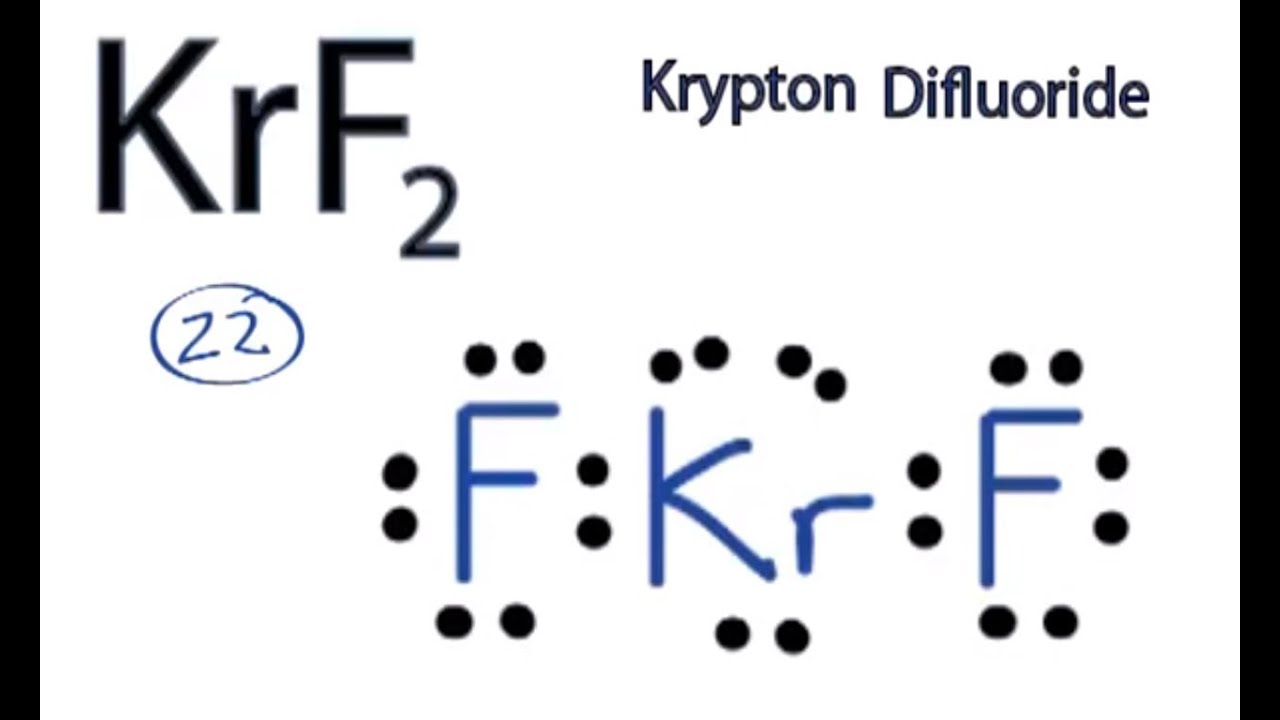
Krf2 Lewis Structure How To Draw The Lewis Structure For Krf2 Krypton Difluoride Youtube
Lone pair electrons occupy more space than bonding electrons.

Krf2 intermolecular forces. Attractive forces and repulsive forces. Force of attraction or repulsion between molecules and neighboring particles. For instance the force between two ions is.
They typically tend to only affect the solid and liquid phases. But much more weakly than a bond. Intermolecular forces are forces that exist between molecules.
That is they arise from the interaction between positively and negatively charged species. The intermolecular potentials for D 2 N 2 O 2 F 2 and CO 2 are determined on the basis of the second virial coeffincients the polarizabilities parallel and perpendicular to the molecular axes and the electric quadrupole moment. And we are going to say intermolecular forces dont influence the chemical properties of a compound they.
However there can be. The repulsive parts of the potentials are taken from the corresponding Kihara core-potentials. Now other than intramolecular forces we have intermolecular forces.
The attractive intermolecular forces are also called van Der Waals forces which in honour of a Dutch scientist Johannes Van der Waals. They result from interactions between permanent induced or temporary electric dipoles. Multiple bonds count as a single pair of electrons.
E KrF 2 K r F 2. Determination of Bond Angles. The intermolecular forces of hydrogen bonding LDFs and.
Using these forces Van der Waals describes the deviation of a real gas from the ideal gas law. Then indicate what type of bonding is holding the atoms together in one molecule of the following. Now intermolecular forces are the forces between different molecules.
For example the covalent bond present within a hydrogen chloride HCl molecule is much stronger than any bonds it may form with neighboring. The presence of lone pair electrons. C O2 O 2.
Intermolecular forces are of two types. So here we have water and it can interact with the compound we are just going to say is B compound B. London forces occur between all molecular substances and noble gases.
NOTE if the molecule is an ionic compound then there is no IMF the ions are all held together by ionic bonds. They chiefly originate from coulombic interactions between charged particles. Tntmduction The simplest example of intermolecular forces is the force between two inert-gas atoms for which the potential energy 11r is a function only of the distance r between the nuclei.
The temporary dipole that results from the motion of the electrons in an atom. Commonly compounds with C-Cl C. Electron pairs in the valence shell orbitals of an atom exert repulsive forces on other electron pairs.
They do not occur in ionic substances. Here and r0 are constants to be determined empirically. Intermolecular forces IMF or secondary forces are the forces which mediate interaction between molecules including forces of attraction or repulsion which act between atoms and other.
B HF H F. Dipole-dipole attractions result from the electrostatic attraction of the partial negative end of one dipolar molecule for the partial positive end of another. Not only are IMFs weaker than bonds-attractive forces due to simultaneous attraction for electrons that exist between 2 nuclei- but they also depend on the type of particle in a sample of matter.
Like covalent and ionic bonds intermolecular interactions are the sum of both attractive and repulsive components. Intermolecular Forces IMFs are attractions between entire molecules due to charge differences. Effects of the octopolar induction are taken into consideration in a unique way.
Intermolecular attractive forces collectively referred to as van der Waals forces are responsible for the behavior of liquids and solids and are electrostatic in nature. The forces of attraction or repulsion existing among the particles of atoms or molecules of a solid liquid or gaseous substance other than the electrostatic force that exists among the positively charged ions and forces that hold atoms of a molecule together ie covalent bonds are called intermolecular forces. List the intermolecular forces present in the following molecules.
Here we examine the solubility of water ethanol hexane and potassium permanganate in each other. Intermolecular forces are electrostatic in nature. That is they are simply attractionsrepulsions obeying Coulombs Law.
The last are called dispersion forces. These forces are weak compared to the intramolecular forces such as the covalent or ionic bonds between atoms in a molecule. Because electrostatic interactions fall off rapidly with increasing distance between molecules intermolecular interactions are most important for solids.
50-200 kJmole Intermolecular force. Van der Waals forces are cohesive attractions between molecules that are already active at long interdistances. Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles atoms molecules or ions.
It is usual to approximate the potential energy Ur between two inert-gas atoms by the Lennard-Jones potential function 11r U0 r0r 2 2r0r6. Intramolecular forces are the forces that hold atoms together within a molecule. D CH3OCH3 C H 3 O C H 3.
Intermolecular forces are electrostatic in nature. The attraction is mainly a result of the electrostatic forces. Their interaction is an intermolecular force interaction.
Intermolecular Forces Moleculesatoms can stick to each other. IMF Intermolecular Forces Worksheet Indicate the strongest IMF holding together thousands of molecules of the following. Figure of intermolecular attraction between two H-Cl molecules and intramolecular attraction within H-Cl molecule.
Repulsion forces are only important when the distance between the atoms falls-below the sum of the van der Waals radii. A C2H2 C 2 H 2. Electron pairs adopt configuration that minimize the electron pair repulsions in the valence shell.
F CH3N H2 C H 3 N H 2.
Bonding Review The Knowledge You Need To Score High 5 Steps To A 5 Ap Chemistry 2015

Krf2 Lewis Structure Hybridization Molecular Geometry And Polarity Techiescientist
Announcements Be Respectful No Electronics Please Ppt Download

Krf2 Lewis Structure Hybridization Molecular Geometry And Polarity Techiescientist

Chapter 5 Kinetic Molecular Theory Keave And Average Velocity
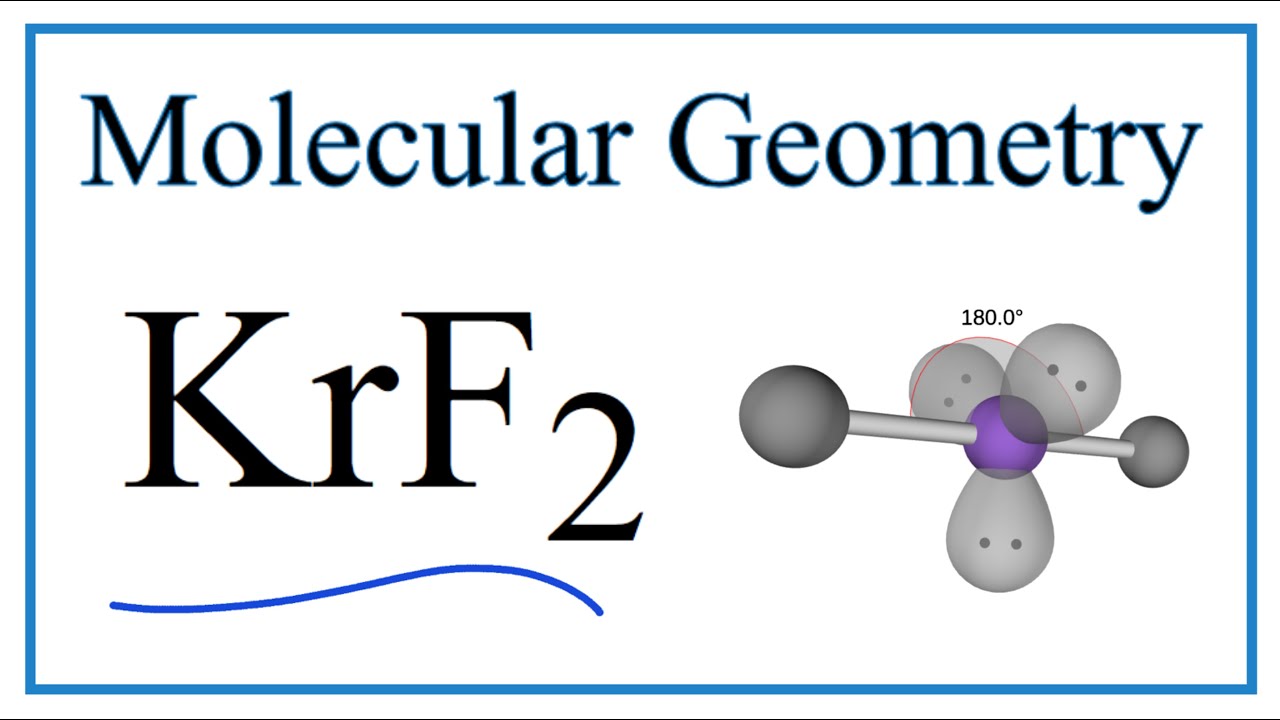
Krf2 Molecular Geometry Bond Angles And Polarity Youtube

Consider A Pure Sample Of Krf2 Molecules Which Of Chegg Com

Chemistry Practice Exam 5 Spring 2014 Katz Pdf Free Download

Is Krf2 Krypton Difluoride Polar Or Nonpolar
Http Web Uvic Ca Mcindoe 101 C101test2abfall2011answerkey Pdf
Announcements Be Respectful No Electronics Please Ppt Download

Krf2 Lewis Structure Hybridization Molecular Geometry And Polarity Techiescientist

Krf2 Lewis Structure Hybridization Molecular Geometry And Polarity Techiescientist

1 Lone Pairs Is Consisted Of A Two Electrons On An Chegg Com

1 Lone Pairs Is Consisted Of A Two Electrons On An Chegg Com



0 Response to "Krf2 Intermolecular Forces"
Posting Komentar